Amygdalanoun
(neuroanatomy) Each one of the two regions of the brain, located as a pair in the medial temporal lobe, believed to play a key role in processing emotions, such as fear and pleasure, in both animals and humans.
Amygdalanoun
An almond.
Amygdalanoun
One of the tonsils of the pharynx.
Amygdalanoun
an almond-shaped neural structure in the anterior part of the temporal lobe of the cerebrum; intimately connected with the hypothalamus and the hippocampus and the cingulate gyrus; as part of the limbic system it plays an important role in motivation and emotional behavior
Amygdala
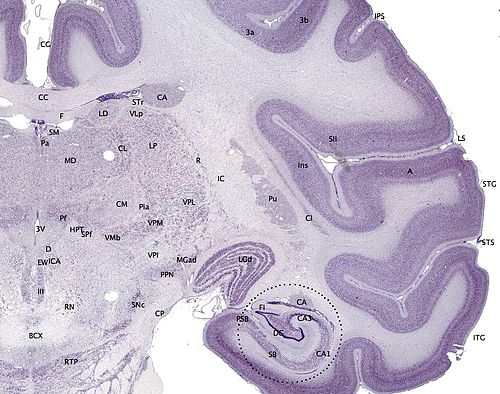
The amygdala (; plural: amygdalae or amygdalas; also corpus amygdaloideum; Latin from Greek, ἀμυγδαλή, amygdalē, 'almond', 'tonsil') is one of two almond-shaped clusters of nuclei located deep and medially within the temporal lobes of the brain's cerebrum in complex vertebrates, including humans. Shown to perform a primary role in the processing of memory, decision-making and emotional responses (including fear, anxiety, and aggression), the amygdalae are considered part of the limbic system.
Hippocampusnoun
(mythological creature) A mythological creature with the front head and forelimbs of a horse and the rear of a dolphin.
Hippocampusnoun
A part of the brain located inside the temporal lobe, consisting mainly of grey matter. It is a component of the limbic system and plays a role in memory and emotion.
Hippocampusnoun
A fabulous monster, with the head and fore quarters of a horse joined to the tail of a dolphin or other fish (Hippocampus brevirostris), - seen in Pompeian paintings, attached to the chariot of Neptune.
Hippocampusnoun
A genus of lophobranch fishes of several species in which the head and neck have some resemblance to those of a horse; - called also sea horse.
Hippocampusnoun
A name applied to either of two ridges of white matter in each lateral ventricle of the brain. The larger is called hippocampus major or simply hippocampus. The smaller, hippocampus minor, is called also ergot and calcar.
Hippocampusnoun
a complex neural structure (shaped like a sea horse) consisting of gray matter and located on the floor of each lateral ventricle; intimately involved in motivation and emotion as part of the limbic system; has a central role in the formation of memories
Hippocampusnoun
seahorses
Hippocampus
The hippocampus (via Latin from Greek ἱππόκαμπος, 'seahorse') is a major component of the brain of humans and other vertebrates. Humans and other mammals have two hippocampi, one in each side of the brain.