Capitalismnoun
(politics) A socio-economic system based on private ownership of resources or capital.
Capitalismnoun
(economics) An economic system based on private ownership of the means of production and their operation for profit.
Capitalismnoun
A socio-economic system based on private property rights, including the private ownership of resources or capital, with economic decisions made largely through the operation of a market unregulated by the state.
Capitalismnoun
An economic system based on the abstraction of resources into the form of privately owned capital, with economic decisions made largely through the operation of a market unregulated by the state.
Capitalismnoun
An economic system based on predominantly private (individual or corporate) investment in and ownership of the means of production, distribution, and exchange of goods and wealth; contrasted with socialism or especially communism, in which the state has the predominant role in the economy.
Capitalismnoun
an economic system based on private ownership of capital
Capitalism
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their operation for profit. Central characteristics of capitalism include capital accumulation, competitive markets, a price system, private property and the recognition of property rights, voluntary exchange and wage labor.
Feudalismnoun
A social system based on personal ownership of resources and personal fealty between a suzerain (lord) and a vassal (subject). Defining characteristics are direct ownership of resources, personal loyalty, and a hierarchical social structure reinforced by religion.
Feudalismnoun
The feudal system; a system by which the holding of estates in land is made dependent upon an obligation to render military service to the king or feudal superior; feudal principles and usages.
Feudalismnoun
the social system that developed in Europe in the 8th C; vassals were protected by lords who they had to serve in war
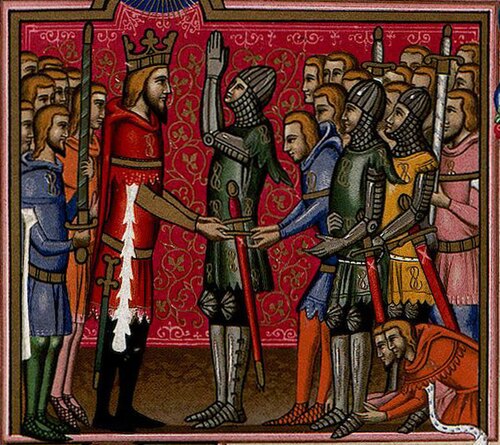
Feudalism
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was the combination of the legal, economic, military, and cultural customs that flourished in Medieval Europe between the 9th and 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a way of structuring society around relationships that were derived from the holding of land in exchange for service or labor.