Centrosomenoun
(cytology) An organelle, near the nucleus in the cytoplasm of most organisms, that controls the organization of its microtubules
Centrosomenoun
A peculiar rounded body lying near the nucleus of a cell. It is regarded as the dynamic element by means of which the machinery of cell division is organized.
Centrosomenoun
small region of cytoplasm adjacent to the nucleus; contains the centrioles and serves to organize the microtubules
Centrosome
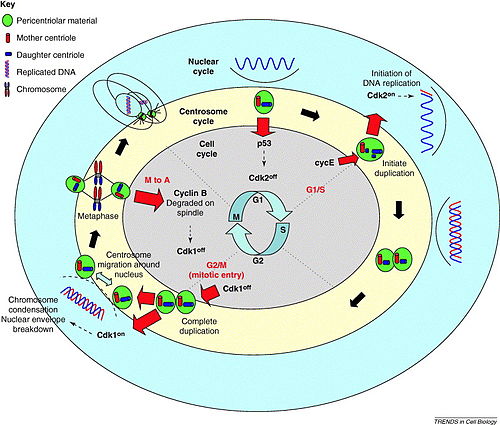
In cell biology, the centrosome (Latin centrum 'center' + Greek sōma 'body') (also called cytocenter) is an organelle that serves as the main microtubule organizing center (MTOC) of the animal cell, as well as a regulator of cell-cycle progression. The centrosome provides structure for the cell.
Centriolenoun
(biology) A barrel-shaped microtubule structure found in most animal cells, important in the process of mitosis (nuclear division).
Centriolenoun
one of two small cylindrical cell organelles composes of nine triplet microtubules, which form the asters during mitosis.
Centriolenoun
one of two small cylindrical cell organelles composes of 9 triplet microtubules; form the asters during mitosis
Centriole
In cell biology a centriole is a cylindrical organelle composed mainly of a protein called tubulin. Centrioles are found in most eukaryotic cells, but are not present in conifers (Pinophyta), flowering plants (angiosperms) and most fungi, and are only present in the male gametes of charophytes, bryophytes, seedless vascular plants, cycads, and Ginkgo.