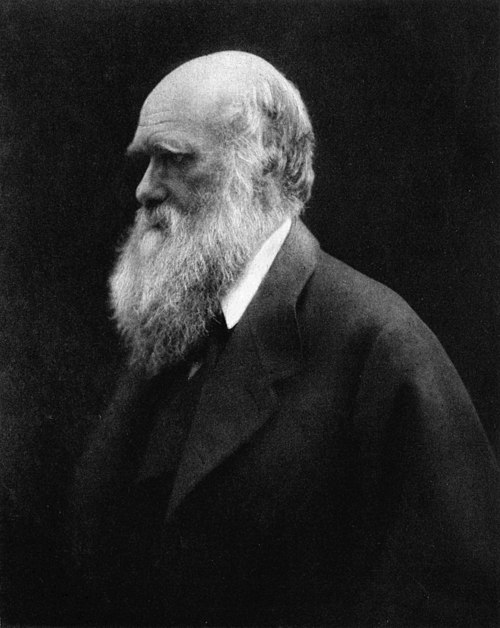Darwinismnoun
.
Darwinismnoun
The theory or doctrines put forth by Darwin. See above.
Darwinismnoun
a theory of organic evolution claiming that new species arise and are perpetuated by natural selection
Darwinism
Darwinism is a theory of biological evolution developed by the English naturalist Charles Darwin (1809–1882) and others, stating that all species of organisms arise and develop through the natural selection of small, inherited variations that increase the individual's ability to compete, survive, and reproduce. Also called Darwinian theory, it originally included the broad concepts of transmutation of species or of evolution which gained general scientific acceptance after Darwin published On the Origin of Species in 1859, including concepts which predated Darwin's theories.
Evolutionnoun
The process of accumulating change.
Evolutionnoun
A progression of change, often branching and diversifying in the process.
Evolutionnoun
(general) Gradual directional change especially one leading to a more advanced or complex form; growth; development.
Evolutionnoun
(biology) The change in the genetic composition of a population over successive generations.
Evolutionnoun
(chemistry) The act or an instance of giving off gas; emission.
Evolutionnoun
(mathematics) The extraction of a root from a quantity.
Evolutionnoun
(military) One of a series of ordered movements.
Evolutionnoun
A turning movement of the body.
Evolutionnoun
The act of unfolding or unrolling; hence, any process of growth or development; as, the evolution of a flower from a bud, or an animal from the egg.
Evolutionnoun
A series of things unrolled or unfolded.
Evolutionnoun
The formation of an involute by unwrapping a thread from a curve as an evolute.
Evolutionnoun
The extraction of roots; - the reverse of involution.
Evolutionnoun
A prescribed movement of a body of troops, or a vessel or fleet; any movement designed to effect a new arrangement or disposition; a maneuver.
Evolutionnoun
A general name for the history of the steps by which any living organism has acquired the morphological and physiological characters which distinguish it; a gradual unfolding of successive phases of growth or development.
Evolutionnoun
That theory of generation which supposes the germ to preëxist in the parent, and its parts to be developed, but not actually formed, by the procreative act; - opposed to epigenesis.
Evolutionnoun
That series of changes under natural law which involves continuous progress from the homogeneous to the heterogeneous in structure, and from the single and simple to the diverse and manifold in quality or function. The process is by some limited to organic beings; by others it is applied to the inorganic and the psychical. It is also applied to explain the existence and growth of institutions, manners, language, civilization, and every product of human activity. The agencies and laws of the process are variously explained by different philosophrs.
Evolutionnoun
a process in which something passes by degrees to a different stage (especially a more advanced or mature stage);
Evolutionnoun
(biology) the sequence of events involved in the evolutionary development of a species or taxonomic group of organisms
Evolutionnoun
the process by which different kinds of living organism are believed to have developed from earlier forms during the history of the earth.
Evolutionnoun
the gradual development of something
Evolutionnoun
the giving off of a gaseous product, or of heat
Evolutionnoun
a pattern of movements or manoeuvres
Evolutionnoun
the extraction of a root from a given quantity.
Evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes that are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction.