Diffractionnoun
(physics) The bending of a wave around an obstacle.
Diffractionnoun
(quantum mechanics) The breaking up of an electromagnetic wave as it passes a geometric structure (e.g. a slit), followed by reconstruction of the wave by interference.
Diffractionnoun
The deflection and decomposition of light in passing by the edges of opaque bodies or through narrow slits, causing the appearance of parallel bands or fringes of prismatic colors, as by the action of a grating of fine lines or bars.
Diffractionnoun
when light passes sharp edges or goes through narrow slits the rays are deflected and produce fringes of light and dark bands
Diffraction
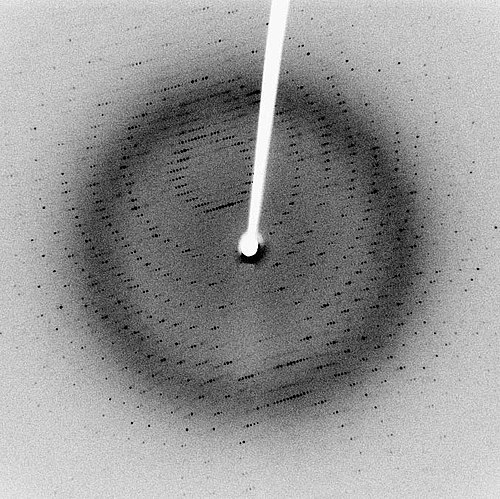
Diffraction refers to various phenomena that occur when a wave encounters an obstacle or opening. It is defined as the bending of waves around the corners of an obstacle or through an aperture into the region of geometrical shadow of the obstacle/aperture.
Refractionnoun
(physics) The turning or bending of any wave, such as a light or sound wave, when it passes from one medium into another of different optical density.
Refractionnoun
(metallurgy) The degree to which a metal or compound can withstand heat
Refractionnoun
The act of refracting, or the state of being refracted.
Refractionnoun
The change in the direction of ray of light, heat, or the like, when it enters obliquely a medium of a different density from that through which it has previously moved.
Refractionnoun
The change in the direction of a ray of light, and, consequently, in the apparent position of a heavenly body from which it emanates, arising from its passage through the earth's atmosphere; - hence distinguished as atmospheric refraction, or astronomical refraction.
Refractionnoun
the change in direction of a propagating wave (light or sound) when passing from one medium to another
Refractionnoun
the amount by which a propagating wave is bent
Refraction
In physics, refraction is the change in direction of a wave passing from one medium to another or from a gradual change in the medium. Refraction of light is the most commonly observed phenomenon, but other waves such as sound waves and water waves also experience refraction.