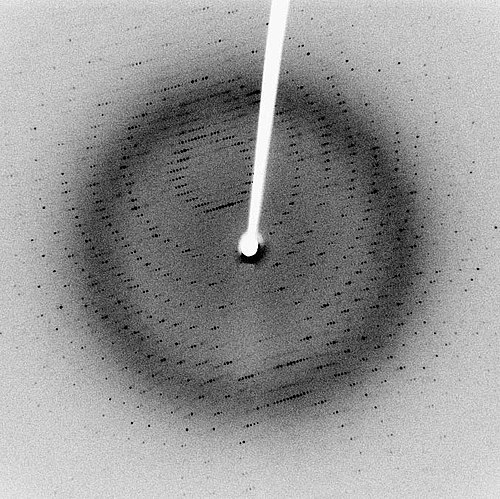
Diffractionnoun
(physics) The bending of a wave around an obstacle.
Diffractionnoun
(quantum mechanics) The breaking up of an electromagnetic wave as it passes a geometric structure (e.g. a slit), followed by reconstruction of the wave by interference.
Diffractionnoun
The deflection and decomposition of light in passing by the edges of opaque bodies or through narrow slits, causing the appearance of parallel bands or fringes of prismatic colors, as by the action of a grating of fine lines or bars.
Diffractionnoun
when light passes sharp edges or goes through narrow slits the rays are deflected and produce fringes of light and dark bands
Diffraction
Diffraction refers to various phenomena that occur when a wave encounters an obstacle or opening. It is defined as the bending of waves around the corners of an obstacle or through an aperture into the region of geometrical shadow of the obstacle/aperture.
Scatteringnoun
A small quantity of something occurring at irregular intervals and dispersed at random points,
Scatteringnoun
(elections) The total number of votes awarded to nonmajor or unlisted candidates.
Scatteringnoun
(physics) The process whereby a beam of waves or particles is dispersed by collisions or similar interactions.
Scatteringadjective
Going or falling in various directions; not united or aggregated; divided among many; as, scattering votes.
Scatteringnoun
Act of strewing about; something scattered.
Scatteringnoun
the physical process in which particles are deflected haphazardly as a result of collisions
Scatteringnoun
a small number dispersed haphazardly;
Scatteringnoun
a light shower that falls in some locations and not others nearby
Scatteringnoun
spreading widely or driving off
Scatteringnoun
the act of scattering
Scatteringadjective
spreading by diffusion
Scattering
Scattering is a term used in physics to describe a wide range of physical processes where moving particles or radiation of some form, such as light or sound, are forced to deviate from a straight trajectory by localized non-uniformities (including particles and radiation) in the medium through which they pass. In conventional use, this also includes deviation of reflected radiation from the angle predicted by the law of reflection.