Funginoun
plural of fungus
Funginoun
(pathology) Spongy, abnormal growth, as granulation tissue formed in a wound
Fungi
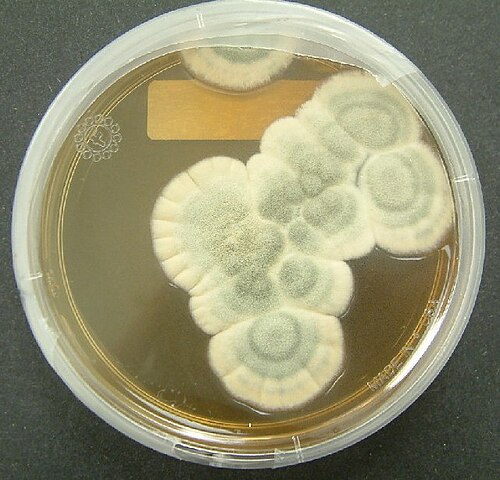
A group of thallophytic plant-like organisms of low organization, destitute of chlorophyll, in which reproduction is mainly accomplished by means of asexual spores, which are produced in a great variety of ways, though sexual reproduction is known to occur in certain Phycomycetes, or so-called algal fungi. They include the molds, mildews, rusts, smuts, mushrooms, toadstools, puff balls, and the allies of each. In the two-kingdom classification system they were classed with the plants, but in the modern five-kingdom classification, they are not classed as plants, but are classed in their own separate kingdom fungi, which includes the phyla Zygomycota (including simple fungi such as bread molds), Ascomycota (including the yeasts), Basidiomycota (including the mushrooms, smuts, and rusts), and Deuteromycota (the fungi imperfecti). Some of the forms, such as the yeasts, appear as single-celled microorganisms, but all of the fungi are are eukaryotic, thus distinguishing them from the prokaryotic microorganisms of the kingdon Monera.
Funginoun
the taxonomic kingdom of lower plants
Funginoun
(pun) the one who buys the drinks
Protozoa
The lowest of the grand divisions of the animal kingdom.
Protozoanoun
in some classifications considered a superphylum or a subkingdom; comprises flagellates; ciliates; sporozoans; amoebas; foraminifers
Protozoa
Protozoa (also protozoan, plural protozoans) is an informal term for a group of single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, that feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic tissues and debris. Historically, protozoans were regarded as , because they often possess animal-like behaviours, such as motility and predation, and lack a cell wall, as found in plants and many algae.