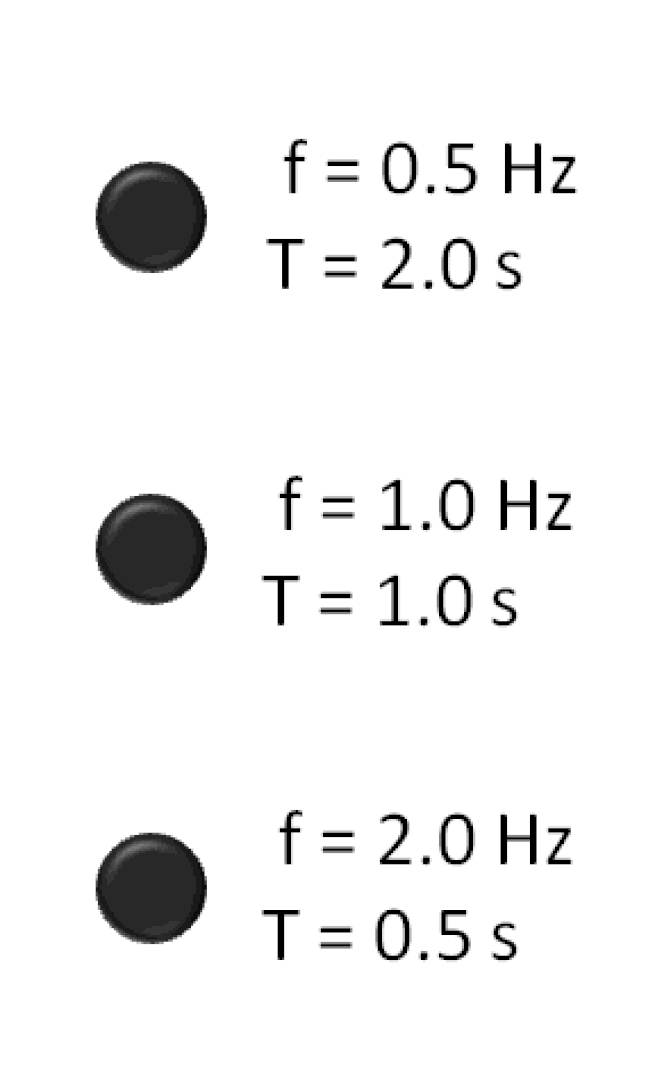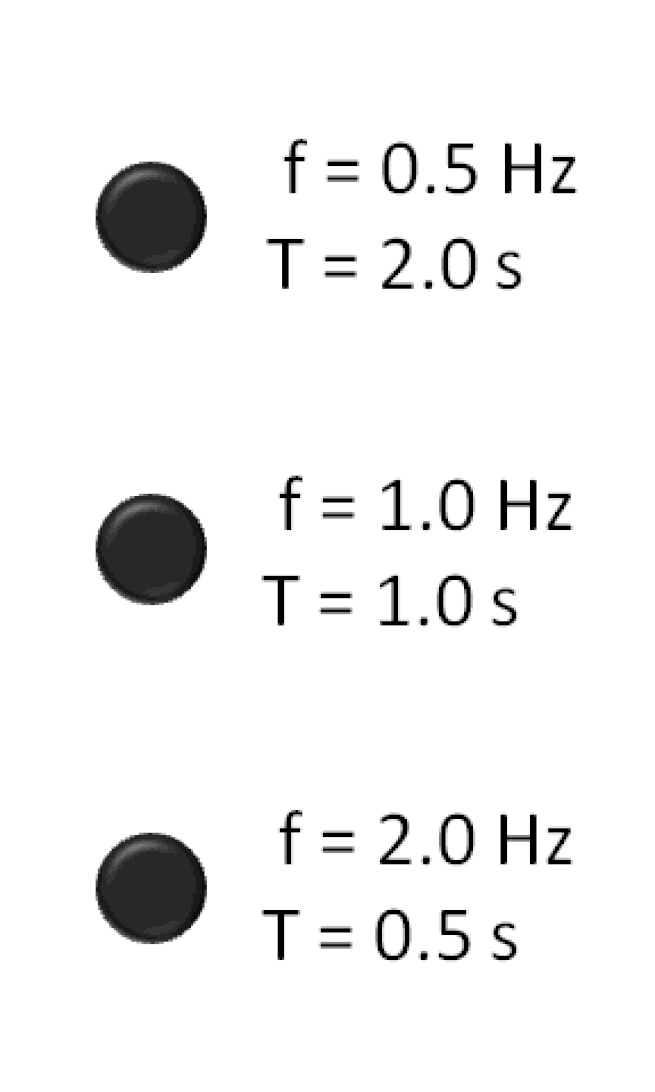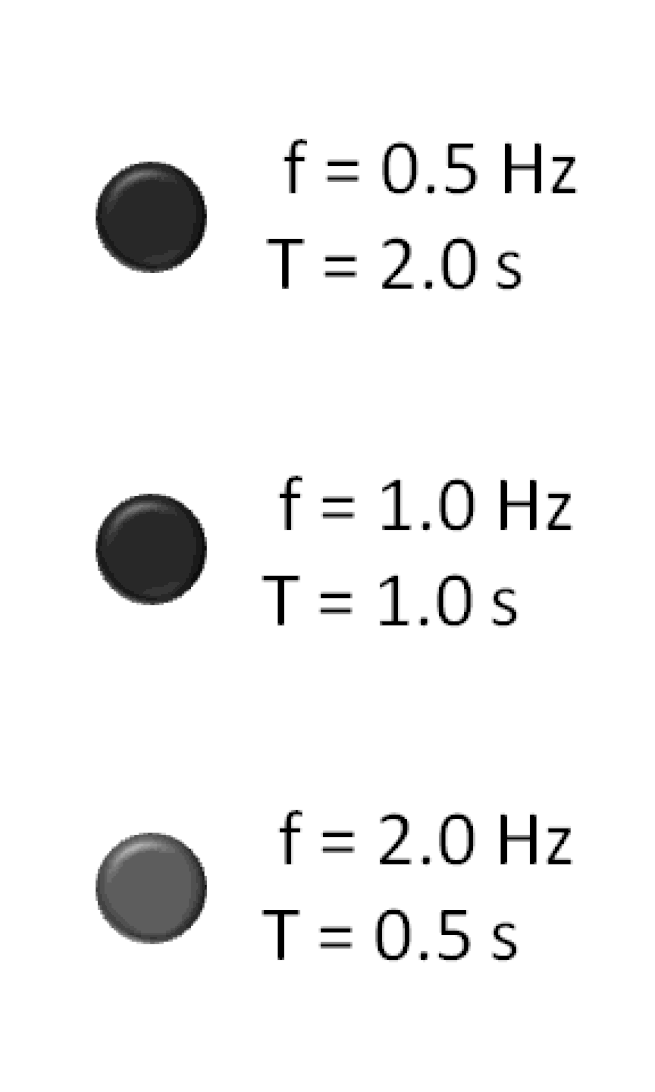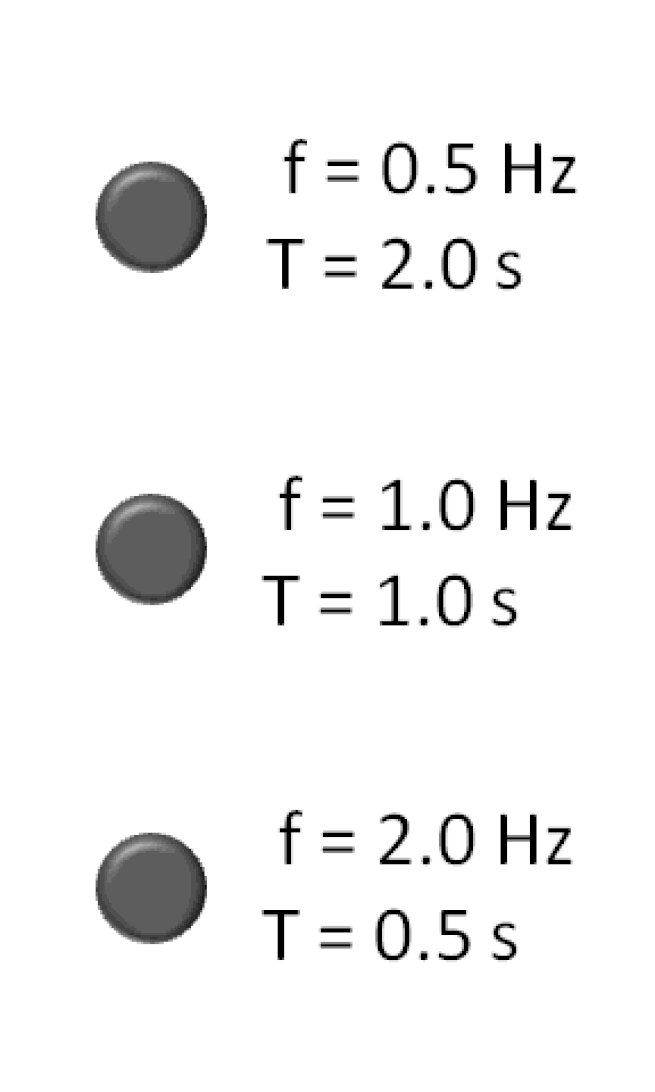Hertznoun
In the International System of Units, the derived unit of frequency; one (period or cycle of any periodic event) per second. Symbol: Hz
Hertznoun
a unit of frequency equal to one cycle per second; it is abbreviated Hz. It is commonly used to specify the frequency of radio waves, and also the clock frequencies in digital computers. For these applications, kilohertz and megahertz are the most commonly used units, derived from hertz.
Hertznoun
the unit of frequency; one Hertz has a periodic interval of one second
Hertznoun
German physicist who was the first to produce electromagnetic waves artificially (1857-1894)
Hertznoun
German physicist who with James Franck proved the existence of the stationary energy states postulated by Bohr (1887-1975)
Hertznoun
the SI unit of frequency, equal to one cycle per second.
Hertz
The hertz (symbol: Hz) is the derived unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI) and is defined as one cycle per second. It is named after Heinrich Rudolf Hertz (1857-1894), the first person to provide conclusive proof of the existence of electromagnetic waves.
Amperenoun
A unit of electrical current, the standard base unit in the International System of Units; colloquially amp. Abbreviation: amp, Symbol: A
Amperenoun
The unit of electric current; - defined by the International Electrical Congress in 1893 and by U. S. Statute as, one tenth of the unit of current of the C. G. S. system of electro-magnetic units, or the practical equivalent of the unvarying current which, when passed through a standard solution of nitrate of silver in water, deposits silver at the rate of 0.001118 grams per second. Called also the international ampère.
Amperenoun
a former unit of electric current (slightly smaller than the SI ampere)
Amperenoun
the basic unit of electric current adopted under the Systeme International d'Unites;
Ampere
The ampere (, US: ; symbol: A), often shortened to amp, is the base unit of electric current in the International System of Units (SI). It is named after André-Marie Ampère (1775–1836), French mathematician and physicist, considered the father of electromagnetism.