Microorganismnoun
(microbiology) An organism that is too small to be seen by the unaided eye, especially a single-celled organism, such as a bacterium.
Microorganismnoun
Any microscopic form of life; a form of life too small to be seen by the naked eye; - particularly applied to bacteria, protozoa, yeasts, and similar organisms, esp. such are supposed to cause infectious diseases.
Microorganismnoun
any organism of microscopic size
Microorganism
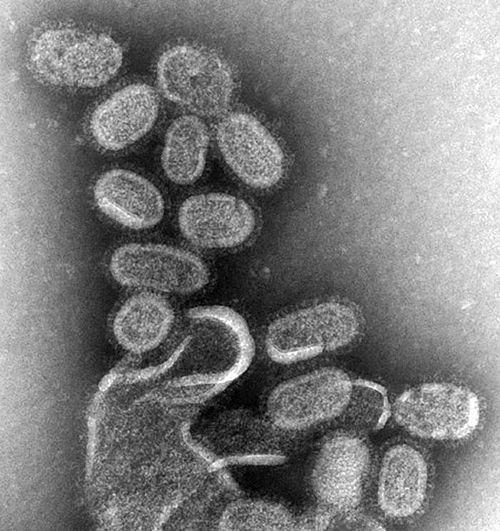
A microorganism, or microbe, is a microscopic organism, which may exist in its single-celled form or a colony of cells. The possible existence of unseen microbial life was suspected from ancient times, such as in Jain scriptures from sixth century BC India.
Pathogennoun
Any organism or substance, especially a microorganism, capable of causing disease, such as bacteria, viruses, protozoa or fungi. Microorganisms are not considered to be pathogenic until they have reached a population size that is large enough to cause disease.
Pathogennoun
Any microorganism which causes disease; a pathogenic organism; an infectious microorganism; a bacterium, virus, or other agent which can cause disease by infection; - opposed to zymogene. The spelling pathogene is now archaic.
Pathogennoun
any disease-producing agent (especially a virus or bacterium or other microorganism)
Pathogen
In biology, a pathogen (Greek: πάθος pathos , and -γενής -genēs ) in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a germ.