Mitosisnoun
(cytology) The division of a cell nucleus in which the genome is copied and separated into two identical halves. It is normally followed by cell division.
Mitosisnoun
See Karyokinesis.
Mitosisnoun
cell division in which the nucleus divides into nuclei containing the same number of chromosomes
Mitosisnoun
a type of cell division that results in two daughter cells each having the same number and kind of chromosomes as the parent nucleus, typical of ordinary tissue growth
Mitosis
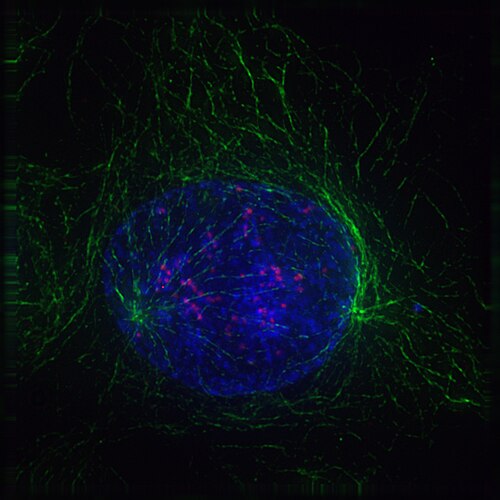
In cell biology, mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. Cell division gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the total number of chromosomes is maintained.
Amitosisnoun
cell division by cleavage of the nucleus without the formation of condensed chromosomes
Amitosisnoun
Cell division in which there is first a simple cleavage of the nucleus without change in its structure (such as the formation of chromosomes), followed by the division of the cytoplasm; direct cell division; - opposed to mitosis. It is not the usual mode of division, and is believed by many to occur chiefly in highly specialized cells which are incapable of long-continued multiplication, in transitory structures, and in those in early stages of degeneration.
Amitosisnoun
the direct method of cell division characterized by simple division of the nucleus without formation of chromosomes
Amitosis
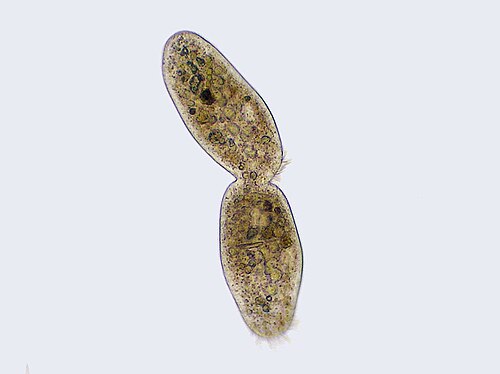
Amitosis (a- + mitosis), also called 'karyostenosis' or direct cell division or binary fission. It is cell proliferation that does not occur by mitosis, the mechanism usually identified as essential for cell division in eukaryotes.