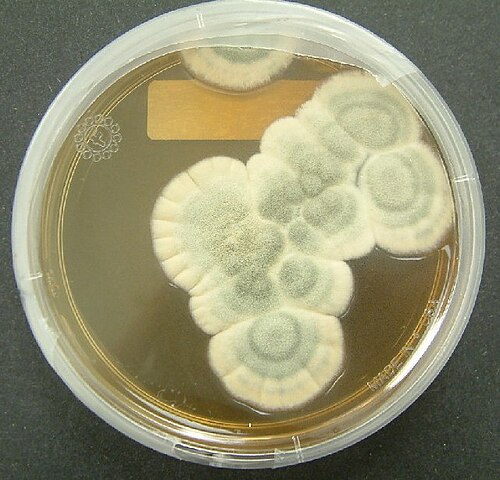
Penicillinnoun
(pharmaceutical drug) Any of a group of narrow-spectrum antibiotics obtained from Penicillium molds or synthesized; they have a beta-lactam structure; most are active against gram-positive bacteria and used in the treatment of various infections and diseases.
Penicillinnoun
Any of a variety of substances having a structure containing a beta-lactam ring fused to a thiirane ring, to which a carboxyl group is attached, but most commonly interpreted as benzyl penicillin. They are notable as powerful antibacterial agents of relatively low toxicity which have found extensive use in medicine for treating bacterial infections. They are categorized as one of the classes of beta-lactam antibiotic. They are produced naturally by some fungi and bacteria, and industrial production processes almost invariably start from some form of the penicillin nucleus produced by fermentation of microorganisms. The fermentation products are then chemically modified to produce derivatives of enhanced potency, safety, or antibacterial spectrum. The first penicillin to see extensive use clinically (during World War II) was penicillin G, also called benzypenicillin, and commonly simply "penicillin".
Penicillinnoun
any of various antibiotics obtained from penicillium molds (or produced synthetically) and used in the treatment of various infections and diseases
Penicillin
Penicillins (P, PCN or PEN) are a group of antibiotics originally obtained from Penicillium moulds, principally P. chrysogenum and P. rubens. Most penicillins in clinical use are chemically synthesised from naturally-produced penicillins.
Methicillinnoun
(pharmaceutical drug) meticillin.
Methicillinnoun
antibiotic drug of the penicillin family used in the treatment of certain staphylococcal infections
Methicillin
Methicillin, also known as meticillin, is a narrow-spectrum β-lactam antibiotic of the penicillin class. Meticillin was discovered in 1960.