Phospholipidnoun
(chemistry) Any lipid, such as lecithin or cephalin, consisting of a diglyceride combined with a phosphate group and a simple organic molecule such as choline or ethanolamine; they are important constituents of biological membranes.
Phospholipidnoun
any of various compounds composed of fatty acids and phosphoric acid and a nitrogenous base; an important constituent of membranes
Phospholipidnoun
a lipid containing a phosphate group in its molecule, e.g. phosphatidylcholine.
Phospholipid
Phospholipids, also known as phosphatides, are a class of lipids whose molecule has a hydrophilic containing a phosphate group, and two hydrophobic derived from fatty acids, joined by a glycerol molecule. Marine phospholipids typically have omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA integrated as part of the phospholipid molecule.
Glycolipidnoun
(biochemistry) An association of a carbohydrate and a phospholipid, such as phosphatidylinositol, found in cell membranes
Glycolipidnoun
(biochemistry) A similar compound lacking a phosphate group
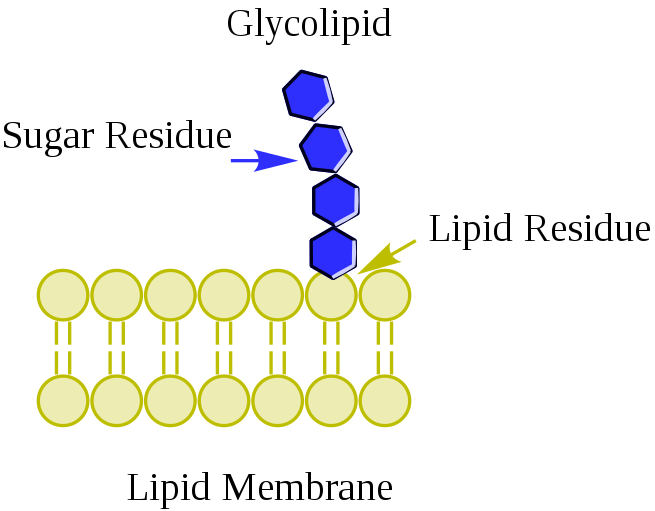
Glycolipid
Glycolipids are lipids with a carbohydrate attached by a glycosidic (covalent) bond. Their role is to maintain the stability of the cell membrane and to facilitate cellular recognition, which is crucial to the immune response and in the connections that allow cells to connect to one another to form tissues.