Pneumonianoun
An acute or chronic inflammation of the lungs caused by viruses, bacteria or other microorganisms, or sometimes by physical or chemical irritants.
Pneumonianoun
Inflammation of the lungs.
Pneumonianoun
respiratory disease characterized by inflammation of the lung parenchyma (excluding the bronchi) with congestion caused by viruses or bacteria or irritants
Pneumonianoun
lung inflammation caused by bacterial or viral infection, in which the air sacs fill with pus and may become solid. Inflammation may affect both lungs (double pneumonia) or only one (single pneumonia).
Pneumonia
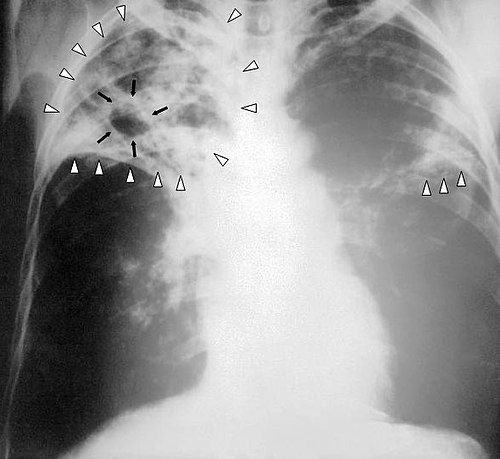
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever and difficulty breathing.
Tuberculosisnoun
(pathology) An infectious disease of humans and animals caused by a species of mycobacterium, usually Mycobacterium tuberculosis, mainly infecting the lungs where it causes tubercles characterized by the expectoration of mucus and sputum, fever, weight loss, and chest pain, and transmitted through inhalation or ingestion of bacteria.
Tuberculosisnoun
A constitutional disease caused by infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis (also called the Tubercle bacillus), characterized by the production of tubercles in the internal organs, and especially in the lungs, where it constitutes the most common variety of pulmonary phthisis (consumption). The Mycobacteria are slow-growing and without cell walls, and are thus not affected by the beta-lactam antibiotics; treatment is difficult, usually requiring simultaneous administration of multiple antibiotics to effect a cure. Prior to availability of antibiotic treatment, the cure required extensive rest, for which special sanatoriums were constructed.
Tuberculosisnoun
infection transmitted by inhalation or ingestion of tubercle bacilli and manifested in fever and small lesions (usually in the lungs but in various other parts of the body in acute stages)
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but can also affect other parts of the body.