Serotoninnoun
(neurotransmitter) An indoleamine neurotransmitter, 5-hydroxytryptamine, that is involved in depression, appetite, etc., and is crucial in maintaining a sense of well-being, security, etc.
Serotoninnoun
a neurotransmitter involved in e.g. sleep and depression and memory
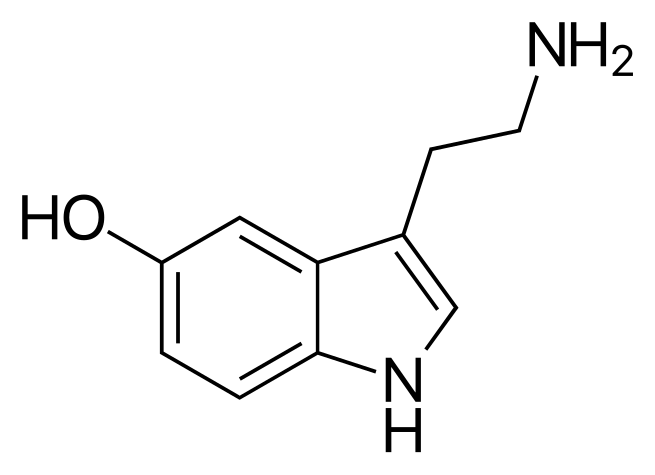
Serotonin
Serotonin () or 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) is a monoamine neurotransmitter. Its biological function is complex and multifaceted, modulating mood, cognition, reward, learning, memory, and numerous physiological processes such as vomiting and vasoconstriction.Biochemically, the indoleamine molecule derives from the amino acid tryptophan, via the (rate-limiting) hydroxylation of the 5 position on the ring (forming the intermediate 5-hydroxytryptophan), and then decarboxylation to produce serotonin.
Dopaminenoun
A monoamine C8H11NO2 that is a decarboxylated form of dopa, present in the body as a neurotransmitter and a precursor of other substances including adrenalin.
Dopaminenoun
a monoamine neurotransmitter found in the brain and essential for the normal functioning of the central nervous system; as a drug (trade names Dopastat and Intropin) it is used to treat shock and hypotension
Dopamine
Dopamine (DA, a contraction of 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine) is a neurotransmitter that plays several important roles in the brain and body. It is an organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families.