Tracheanoun
(anatomy) A thin-walled, cartilaginous tube connecting the larynx to the bronchi; the windpipe.
Tracheanoun
Xylem vessel.
Tracheanoun
(entomology) One of the cuticle-lined primary tubes in the respiratory system of an insect, which extend throughout its body.
Tracheanoun
The windpipe. See Illust. of Lung.
Tracheanoun
One of the respiratory tubes of insects and arachnids.
Tracheanoun
One of the large cells in woody tissue which have spiral, annular, or other markings, and are connected longitudinally so as to form continuous ducts.
Tracheanoun
membranous tube with cartilaginous rings that conveys inhaled air from the larynx to the bronchi
Tracheanoun
one of the tubules forming the respiratory system of most insects and many arachnids
Trachea
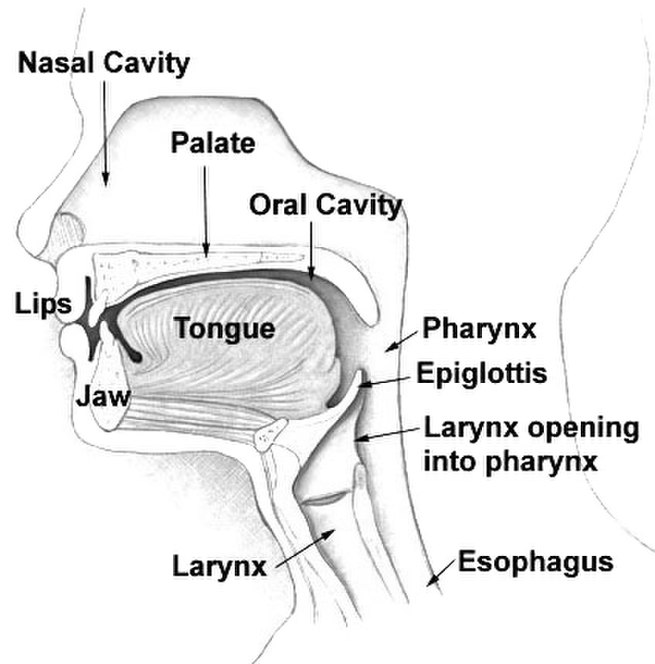
The trachea, also known as the windpipe, is a cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all air-breathing animals with lungs. The trachea extends from the larynx and branches into the two primary bronchi.
Pharynxnoun
(anatomy) The part of the alimentary canal and respiratory tract that extends from the back of the mouth and nasal cavity to the larynx and esophagus.
Pharynxnoun
The part of the alimentary canal between the cavity of the mouth and the esophagus. It has one or two external openings through the nose in the higher vertebrates, and lateral branchial openings in fishes and some amphibias.
Pharynxnoun
the passage to the stomach and lungs; in the front part of the neck below the chin and above the collarbone
Pharynx
The pharynx (plural: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the oesophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its structure varies across species.